Starlink is a group of satellites that SpaceX uses to give 50 countries access to the Internet via satellite. It also wants to have mobile phone service worldwide by 2023. In 2019, SpaceX began sending out Starlink satellites.
The Starlink research, development, manufacturing, and orbit control teams work at the SpaceX satellite development center in Redmond, Washington. SpaceX said in May 2018 that the project to design, build, and launch the constellation would take at least ten years and cost at least $10 billion. SpaceX expects its satellite constellation to bringing in more than $30 billion by 2025.
Astronomers are worried about how the constellation will affect astronomy from the ground and how the satellites will add to an already crowded orbit. SpaceX has tried to ease astronomy worries by changing Starlink satellites to make them less bright when working. The satellites have Hall thrusters powered by krypton or argon, allowing them to get out of orbit when their time is up. Also, the satellites are made to avoid collisions on their own based on tracking information that is sent back to them.
Where can I get a piece of that?

Starlink is mostly for people between latitudes 33.6° and 54.9° in the US, Canada, New Zealand, Australia, and a few European countries.
Most of the US is within these latitudes, and we found that most Starlink customers live in northern states like Washington, Wisconsin, and Michigan. But a few lucky people in some southern states, like Missouri, also get Starlink service.
Starlink can go far and connect even the most isolated places on Earth.
How Starlink Works?
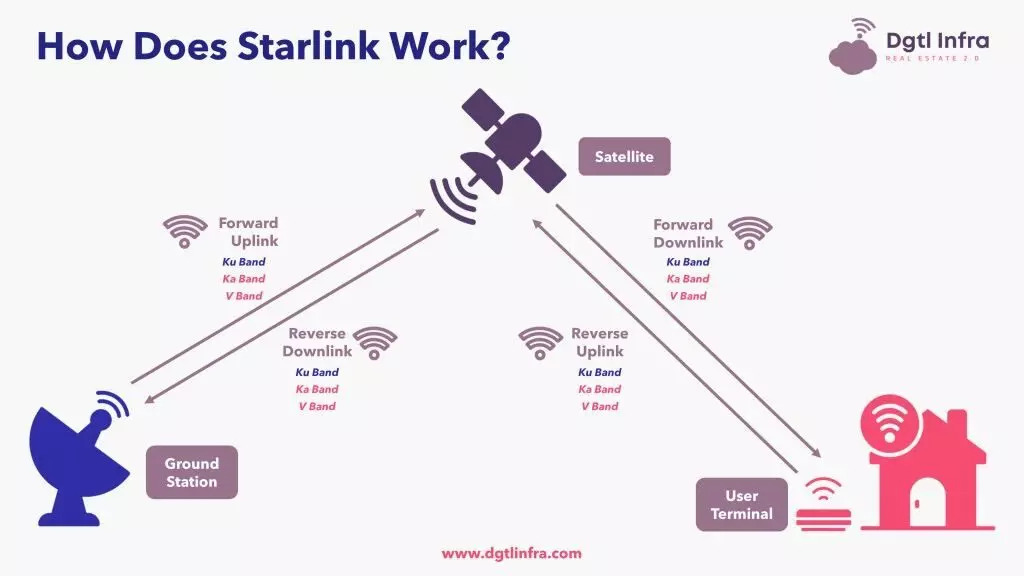
Most satellite Internet services come from single geostationary satellites that circle the Earth at 35,786 km. As a result, the round-trip data time between the user and the satellite, also called latency, is long. It makes supporting streaming, online gaming, video calls, and other high-data-rate activities nearly impossible.
Starlink is a group of thousands of satellites that orbit the Earth much closer, at about 550 km, and cover the whole world. Because Starlink satellites are in a low orbit, latency is much lower—about 20 ms instead of 600 ms or more.
History of Starlink

As part of the Strategic Defense Initiative, constellations of satellites in low Earth orbit were first thought of in the mid-1980s.
It led to Brilliant Pebbles, where weapons were to be set up in orbit to intercept ballistic missiles quickly. Low-latency communication was also a possibility. In the 1990s, this led to several commercial mega-constellations with about 100 satellites, such as Celestron, Teledesic, Iridium, and Globalstar. But by the time the dot-com bubble burst, all of the companies had gone bankrupt, partly because the costs of starting up were too high.
Larry Williams, the Vice President of Strategic Relations at SpaceX and the Vice President of Teledesic’s “Internet in the sky” program, opened the SpaceX Washington DC office in 2004.
As part of a “shared strategic vision,” SpaceX bought a piece of Surrey Satellite Technology (SSTL) in June of that year. At the time, SSTL was working on putting the Internet in space. But SpaceX’s share was eventually sold back to EADS Astrium in 2008 after the company changed its focus to navigation and Earth observation.
Early in 2014, Elon Musk and Greg Wyler were planning WorldVu, a group of about 700 satellites that would be more than ten times the size of the largest satellite group at the time, Iridium. But in June 2014, these talks broke down, and SpaceX instead sent an application to the ITU under the name STEAM through the Norway telecom regulator. In its 2016 application to the Federal Communications Commission to get a license for Starlink, SpaceX confirmed the link (FCC). SpaceX trademarked Starlink in the United States for their satellite broadband network. The name came from the book “The Fault in Our Stars.”
Thanks for reading Huzzed. Stay tuned for more content 🙂









